Sharing Jupyter Notebooks using Binder
Overview
Teaching: 60 min
Exercises: 60 minQuestions
How can we share Jupyter Notebook so they are interactive, can be run, and modified?
What does it mean for code to “depend” on software?”
How can we explicitly define the dependencies for our code?”
Objectives
Create a shareable interactive binder for your online Jupyter notebooks.”
Create a requirements file listing dependencies for the notebooks in your repository.”
Important notice
This lesson has been taken from https://reproducible-science-curriculum.github.io/sharing-RR-Jupyter/ and is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution license. The following is a human-readable summary of (and not a substitute for) the full legal text of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Reproducible computing environments with Binder
A short intro on Binder
Authors: Chris Holdgraf, M Pacer
Your jupyter dashboards in mybinder
Preparing your github repository for Binder
We would like to publish all the codes in our repository with Binder. To be Binder-compliant, we need to add configurations files (one or more text files) that specify the requirements for building your project’s code:
Sharing our Python environment (environment.yml)
This approach is recommended when all the additional packages/libraries you need are part of conda. Be aware that conda is a source package management system and is not only used for python. Many packages/libraries, independent of python/R are made available via conda, so the best is to first check online whether your package is already available via conda.
name: jupyter_dashboards_workshop
channels:
- tim_shawver
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python>3.6
- notebook>5.2
- jupyter_dashboards
- jupyter_dashboards_bundlers
- matplotlib
- folium
- ipywidgets=7
- qgrid
- plotly
- beakerx
This file must be placed in the root directory of your reprository on Gitub.
Test and launch your Github repository withBinder.
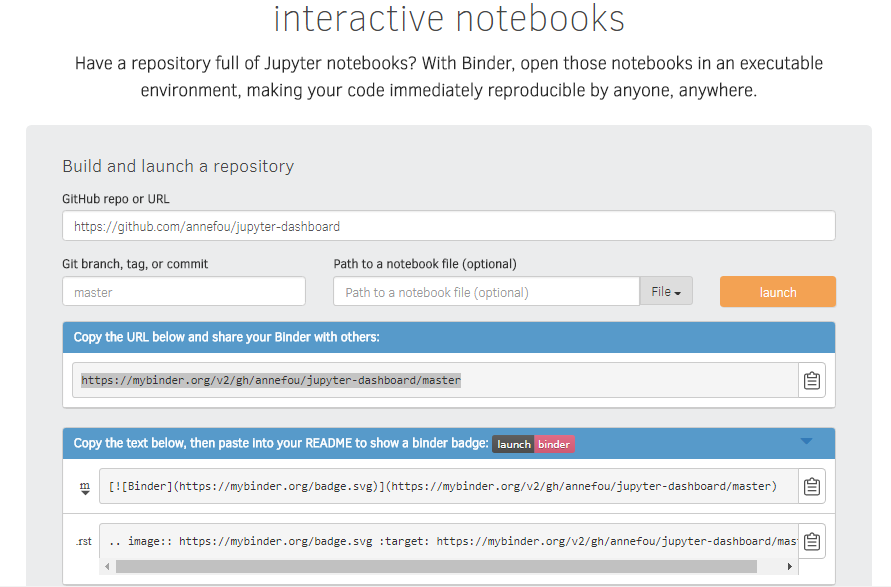
Sharing our complete workflow
Using environment.yml, we can run all our notebooks except those dealing with the SNOWPACK model (snow and land-surface model). To share our computational environment, SNOWPACK needs to be installed. SNOWPACK is not available as a conda package so we will need to install it manually.
- apt.txt : contains all the debian packages that should be installed for installing and running SNOWPACK. C/C++ GNU compilers are available (SNOWPACK is written in C++) but to compile SNOWPACK, we need also cmake which is not available by default:
cmake
-
environment.yml (same as before i.e. with all the conda packages we need)
-
postBuild
#!/bin/bash
# Installation of SNOWPACK a multi-purpose snow and land-surface model, which focuses on a detailed description of the mass and energy exchange between the snow, the atmosphere and optionally with the vegetation cover and the soil. It also includes a detailed treatment of mass and energy fluxes within these media.
export PREFIX="$(python -c 'import sys; print(sys.prefix)')"
work="$PWD"
# Get METEOI library and install:
wget https://models.slf.ch/p/meteoio/downloads/get/MeteoIO-2.7.0-src.tar.gz
tar zxf MeteoIO-2.7.0-src.tar.gz
cd MeteoIO-2.7.0-src
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX
make
make install
cd $work
rm -rf MeteoIO*
# Get SNOWPACK source code and install:
wget https://models.slf.ch/p/snowpack/downloads/get/Snowpack-3.4.5-src.tar.gz
tar zxf Snowpack-3.4.5-src.tar.gz
cd Snowpack-3.4.5-src
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX -DCMAKE_METEOI_ROOT=$PREFIX
make
make install
rm -rf Snowpack*
Note
This file must be executable to be used with repo2docker. To do this, run the following on Linux/Mac-OSX:
chmod +x postBuildOn Windows (to be done before you commit your file):
git update-index --chmod=+x postBuild
Launch your computational environment on Binder
- Start your complete computational environment on Binder
- Try to execute your dashboard
- Check the exectuable called
snowpackis available in your Binder environment
Publish your dashboards in mybinder
- Create a shareable Binder link
- Update your github repository to display shareable Binder link for each of your dashboards
We make two exercises: one with environment.yml (adding conda packages) and one with an entire workflow (apt.txt, environment.yml and postBuild).
Key Points
Binder provides an environment that runs and interactively serves your Jupyter notebooks.
Use
environment.ymlor share your complete computational environment (apt.txt, environment.yml and postBuild) to specify dependencies beyond the Jupyter notebook execution environment itself.