Introduction
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What is NCL?
How to invoke NCL from the command line?
Objectives
Learn what is NCL
Learn how to start NCL
Learn about the netCDF data model
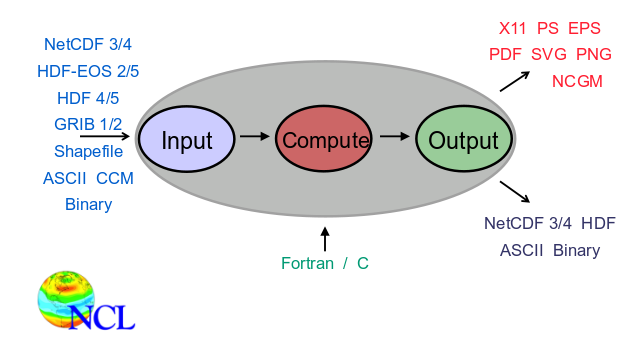
What is NCL?
NCAR Command Language is an Integrated Processing Environment. NCL syntax is close to python or matlab.
;================================================;
; maponly_1.ncl
;================================================;
;
; Concepts illustrated:
; - Drawing a default cylindrical equidistant map
;
;================================================;
;
; These files are loaded by default in NCL V6.2.0 and newer
; load "$NCARG_ROOT/lib/ncarg/nclscripts/csm/gsn_code.ncl"
; load "$NCARG_ROOT/lib/ncarg/nclscripts/csm/gsn_csm.ncl"
; ================================================;
begin
wks = gsn_open_wks("png","maponly") ; send graphics to PNG file
plot = gsn_csm_map(wks,False) ; draw global map
end
Ncl is an interpreted language (not compiled)
- Like python, R, matlab
- Unlike C, C++, fortran
- Many operations implemented in C/fortran under the hood = fast performance
- Interpreter is invoked via the “ncl” command:
How to run it?
$ ncl
Copyright (C) 1995-2015 - All Rights Reserved
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
NCAR Command Language Version 6.3.0
The use of this software is governed by a License Agreement.
See http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/ for more details.
ncl 0>
Pros
- Support netCDF-3/4, HDF-4/5, and GRIB-1/2
- Common data structure: NetCDF model
- Many useful & unique Application Functions
- Publication quality graphics out of the box
- Consistent documentation
- Many examples to get you started
- Excellent Support
Cons
- Interactive environment is rather crude
- No debugger at user level
What’s required to run it
- A Unix-like environment (on Windows, you would need cygwin)
- Some knowledge of bash shell commands (see http://swcarpentry.github.io/shell-novice/) to get a short introduction to bash shell)
- An editor (nano, atom, emacs, etc.)
Running NCL interactively
Like for python or R, we can start ncl and enter ncl commands one after the other:
pi = 4.0 * atan(1.0)
print(pi)
$ ncl
Copyright (C) 1995-2015 - All Rights Reserved
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
NCAR Command Language Version 6.3.0
The use of this software is governed by a License Agreement.
See http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/ for more details.
ncl 0> pi=4.0*atan(1.0)
ncl 1> print(pi)
Variable: pi
Type: float
Total Size: 4 bytes
1 values
Number of Dimensions: 1
Dimensions and sizes: [1]
Coordinates:
(0) 3.141593
ncl 2>
It is useful for testing your NCL installation but not recommended. We usually create a text file where we write our program and then execute it.
For instance, let’s create a new file called test.ncl with your favourite editor:
nano test.ncl
Then store these two lines in test.ncl:
pi = 4.0 * atan(1.0)
print(pi)
Save your file. With nano, use CTRL (Control key on your keyboard) and x (key x) and enter (key Return on your keyboard).
To execute your ncl script:
ncl test.ncl
Copyright (C) 1995-2015 - All Rights Reserved
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
NCAR Command Language Version 6.3.0
The use of this software is governed by a License Agreement.
See http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/ for more details.
Variable: pi
Type: float
Total Size: 4 bytes
1 values
Number of Dimensions: 1
Dimensions and sizes: [1]
Coordinates:
(0) 3.141593
Your ncl script may take a few seconds or a few hours depending on its complexity and how much data you are processing. It is therefore recommended to start your NCL script in background so you can logout from your computer and still run your script:
nohup ncl test.ncl > log_ncl.txt &
The output of your NCL script will then be stored in log_ncl.txt (you can use nano or any other editor to inspect its content).
NCL command line structure
To get the list of available options, you can use:
ncl -h
Usage: ncl -fhnopxQV <args> <file.ncl>
-f: use new file structure and NetCDF4 features when possible
-h: print this message and exit
-n: don't enumerate values in print()
-o: retain former behavior for certain backwards-incompatible changes
-p: don't page output from the system() command
-x: echo NCL commands
-Q: turn off echo of NCL version and copyright info
-V: print NCL version and exit
- Some options modify behavior
- Others print information and exit
- May be combined:
ncl –np test.ncl
The NetCDF data model à NCL’s data model
Why is this important?
- NCL’s variable model is based upon NetCDF’s variable model.
- NCL makes GRIB, HDF, HDF-EOS look like NetCDF
- This consistent and uniform view of disparate file formats is a very powerful feature!
Implication of using NetCDF structured, binary file format
- Can’t view contents directly from command-line
- Use tools like ncdump
NetCDF array-like data
- Common in atmospheric science and other science and engineering disciplines that employ finite-element methods.
- Comprised of variables, dimensions, attributes
A bit more on netCDF with ncdump
Using the online command ncdump -h allows to get metadata information on your netCDF file. Let’s take a history file of CESM CAM model:
ncdump -h
netcdf f2000.T31T31.control.cam.h0.0007-08-29-00000 {
dimensions:
lat = 48 ;
lon = 96 ;
time = UNLIMITED ; // (30 currently)
nbnd = 2 ;
chars = 8 ;
lev = 30 ;
ilev = 31 ;
variables:
double lev(lev) ;
lev:long_name = "hybrid level at midpoints (1000*(A+B))" ;
lev:units = "level" ;
lev:positive = "down" ;
lev:standard_name = "atmosphere_hybrid_sigma_pressure_coordinate" ;
lev:formula_terms = "a: hyam b: hybm p0: P0 ps: PS" ;
double hyam(lev) ;
hyam:long_name = "hybrid A coefficient at layer midpoints" ;
double hybm(lev) ;
hybm:long_name = "hybrid B coefficient at layer midpoints" ;
double ilev(ilev) ;
ilev:long_name = "hybrid level at interfaces (1000*(A+B))" ;
ilev:units = "level" ;
ilev:positive = "down" ;
ilev:standard_name = "atmosphere_hybrid_sigma_pressure_coordinate" ;
ilev:formula_terms = "a: hyai b: hybi p0: P0 ps: PS" ;
double hyai(ilev) ;
hyai:long_name = "hybrid A coefficient at layer interfaces" ;
double hybi(ilev) ;
hybi:long_name = "hybrid B coefficient at layer interfaces" ;
double P0 ;
P0:long_name = "reference pressure" ;
P0:units = "Pa" ;
double time(time) ;
time:long_name = "time" ;
time:units = "days since 0001-01-01 00:00:00" ;
time:calendar = "noleap" ;
time:bounds = "time_bnds" ;
int date(time) ;
date:long_name = "current date (YYYYMMDD)" ;
int datesec(time) ;
datesec:long_name = "current seconds of current date" ;
double lat(lat) ;
lat:long_name = "latitude" ;
lat:units = "degrees_north" ;
double lon(lon) ;
lon:long_name = "longitude" ;
lon:units = "degrees_east" ;
double time_bnds(time, nbnd) ;
time_bnds:long_name = "time interval endpoints" ;
char date_written(time, chars) ;
char time_written(time, chars) ;
int ntrm ;
ntrm:long_name = "spectral truncation parameter M" ;
int ntrn ;
ntrn:long_name = "spectral truncation parameter N" ;
int ntrk ;
ntrk:long_name = "spectral truncation parameter K" ;
int ndbase ;
ndbase:long_name = "base day" ;
int nsbase ;
nsbase:long_name = "seconds of base day" ;
int nbdate ;
nbdate:long_name = "base date (YYYYMMDD)" ;
int nbsec ;
nbsec:long_name = "seconds of base date" ;
int mdt ;
mdt:long_name = "timestep" ;
mdt:units = "s" ;
int nlon(lat) ;
nlon:long_name = "number of longitudes" ;
int wnummax(lat) ;
wnummax:long_name = "cutoff Fourier wavenumber" ;
double gw(lat) ;
gw:long_name = "gauss weights" ;
int ndcur(time) ;
ndcur:long_name = "current day (from base day)" ;
int nscur(time) ;
nscur:long_name = "current seconds of current day" ;
double co2vmr(time) ;
co2vmr:long_name = "co2 volume mixing ratio" ;
double ch4vmr(time) ;
ch4vmr:long_name = "ch4 volume mixing ratio" ;
double n2ovmr(time) ;
n2ovmr:long_name = "n2o volume mixing ratio" ;
double f11vmr(time) ;
f11vmr:long_name = "f11 volume mixing ratio" ;
double f12vmr(time) ;
f12vmr:long_name = "f12 volume mixing ratio" ;
double sol_tsi(time) ;
sol_tsi:long_name = "total solar irradiance" ;
sol_tsi:units = "W/m2" ;
int nsteph(time) ;
nsteph:long_name = "current timestep" ;
float AEROD_v(time, lat, lon) ;
AEROD_v:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
AEROD_v:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
AEROD_v:units = "1" ;
AEROD_v:long_name = "Total Aerosol Optical Depth in visible band" ;
AEROD_v:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ANRAIN(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
ANRAIN:mdims = 1 ;
ANRAIN:units = "m-3" ;
ANRAIN:long_name = "Average rain number conc" ;
ANRAIN:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ANSNOW(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
ANSNOW:mdims = 1 ;
ANSNOW:units = "m-3" ;
ANSNOW:long_name = "Average snow number conc" ;
ANSNOW:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AODDUST1(time, lat, lon) ;
AODDUST1:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
AODDUST1:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
AODDUST1:units = "" ;
AODDUST1:long_name = "Aerosol optical depth 550 nm model 1 from dust" ;
AODDUST1:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AODDUST3(time, lat, lon) ;
AODDUST3:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
AODDUST3:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
AODDUST3:units = "" ;
AODDUST3:long_name = "Aerosol optical depth 550 nm model 3 from dust" ;
AODDUST3:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AODVIS(time, lat, lon) ;
AODVIS:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
AODVIS:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
AODVIS:units = "" ;
AODVIS:long_name = "Aerosol optical depth 550 nm" ;
AODVIS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AQRAIN(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AQRAIN:mdims = 1 ;
AQRAIN:units = "kg/kg" ;
AQRAIN:long_name = "Average rain mixing ratio" ;
AQRAIN:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AQSNOW(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AQSNOW:mdims = 1 ;
AQSNOW:units = "kg/kg" ;
AQSNOW:long_name = "Average snow mixing ratio" ;
AQSNOW:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AREI(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AREI:mdims = 1 ;
AREI:units = "Micron" ;
AREI:long_name = "Average ice effective radius" ;
AREI:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AREL(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AREL:mdims = 1 ;
AREL:units = "Micron" ;
AREL:long_name = "Average droplet effective radius" ;
AREL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AWNC(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AWNC:mdims = 1 ;
AWNC:units = "m-3" ;
AWNC:long_name = "Average cloud water number conc" ;
AWNC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float AWNI(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
AWNI:mdims = 1 ;
AWNI:units = "m-3" ;
AWNI:long_name = "Average cloud ice number conc" ;
AWNI:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDEN1(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDEN1:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN1:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN1:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDEN1:long_name = "Aerosol burden mode 1" ;
BURDEN1:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDEN2(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDEN2:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN2:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN2:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDEN2:long_name = "Aerosol burden mode 2" ;
BURDEN2:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDEN3(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDEN3:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN3:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDEN3:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDEN3:long_name = "Aerosol burden mode 3" ;
BURDEN3:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENBC(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENBC:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENBC:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENBC:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENBC:long_name = "Black carbon aerosol burden" ;
BURDENBC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENDUST(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENDUST:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENDUST:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENDUST:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENDUST:long_name = "Dust aerosol burden" ;
BURDENDUST:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENPOM(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENPOM:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENPOM:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENPOM:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENPOM:long_name = "POM aerosol burden" ;
BURDENPOM:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENSEASALT(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENSEASALT:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSEASALT:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSEASALT:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENSEASALT:long_name = "Seasalt aerosol burden" ;
BURDENSEASALT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENSO4(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENSO4:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSO4:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSO4:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENSO4:long_name = "Sulfate aerosol burden" ;
BURDENSO4:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float BURDENSOA(time, lat, lon) ;
BURDENSOA:_FillValue = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSOA:missing_value = 1.e+36f ;
BURDENSOA:units = "kg/m2" ;
BURDENSOA:long_name = "SOA aerosol burden" ;
BURDENSOA:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CCN3(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
CCN3:mdims = 1 ;
CCN3:units = "#/cm3" ;
CCN3:long_name = "CCN concentration at S=0.1%" ;
CCN3:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CDNUMC(time, lat, lon) ;
CDNUMC:units = "1/m2" ;
CDNUMC:long_name = "Vertically-integrated droplet concentration" ;
CDNUMC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDHGH(time, lat, lon) ;
CLDHGH:units = "fraction" ;
CLDHGH:long_name = "Vertically-integrated high cloud" ;
CLDHGH:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDICE(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
CLDICE:mdims = 1 ;
CLDICE:units = "kg/kg" ;
CLDICE:long_name = "Grid box averaged cloud ice amount" ;
CLDICE:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDLIQ(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
CLDLIQ:mdims = 1 ;
CLDLIQ:units = "kg/kg" ;
CLDLIQ:long_name = "Grid box averaged cloud liquid amount" ;
CLDLIQ:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDLOW(time, lat, lon) ;
CLDLOW:units = "fraction" ;
CLDLOW:long_name = "Vertically-integrated low cloud" ;
CLDLOW:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDMED(time, lat, lon) ;
CLDMED:units = "fraction" ;
CLDMED:long_name = "Vertically-integrated mid-level cloud" ;
CLDMED:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLDTOT(time, lat, lon) ;
CLDTOT:units = "fraction" ;
CLDTOT:long_name = "Vertically-integrated total cloud" ;
CLDTOT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float CLOUD(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
CLOUD:mdims = 1 ;
CLOUD:units = "fraction" ;
CLOUD:long_name = "Cloud fraction" ;
CLOUD:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float DCQ(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
DCQ:mdims = 1 ;
DCQ:units = "kg/kg/s" ;
DCQ:long_name = "Q tendency due to moist processes" ;
DCQ:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float DMS_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
DMS_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
DMS_SRF:long_name = "DMS in bottom layer" ;
DMS_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float DTCOND(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
DTCOND:mdims = 1 ;
DTCOND:units = "K/s" ;
DTCOND:long_name = "T tendency - moist processes" ;
DTCOND:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float DTH(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
DTH:mdims = 1 ;
DTH:units = "K/s" ;
DTH:long_name = "T horizontal diffusive heating" ;
DTH:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float DTV(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
DTV:mdims = 1 ;
DTV:units = "K/s" ;
DTV:long_name = "T vertical diffusion" ;
DTV:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float EMISCLD(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
EMISCLD:mdims = 1 ;
EMISCLD:units = "1" ;
EMISCLD:long_name = "cloud emissivity" ;
EMISCLD:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FICE(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
FICE:mdims = 1 ;
FICE:units = "fraction" ;
FICE:long_name = "Fractional ice content within cloud" ;
FICE:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLDS(time, lat, lon) ;
FLDS:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLDS:units = "W/m2" ;
FLDS:long_name = "Downwelling longwave flux at surface" ;
FLDS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLNS(time, lat, lon) ;
FLNS:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLNS:units = "W/m2" ;
FLNS:long_name = "Net longwave flux at surface" ;
FLNS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLNSC(time, lat, lon) ;
FLNSC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLNSC:units = "W/m2" ;
FLNSC:long_name = "Clearsky net longwave flux at surface" ;
FLNSC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLNT(time, lat, lon) ;
FLNT:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLNT:units = "W/m2" ;
FLNT:long_name = "Net longwave flux at top of model" ;
FLNT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLNTC(time, lat, lon) ;
FLNTC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLNTC:units = "W/m2" ;
FLNTC:long_name = "Clearsky net longwave flux at top of model" ;
FLNTC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLUT(time, lat, lon) ;
FLUT:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLUT:units = "W/m2" ;
FLUT:long_name = "Upwelling longwave flux at top of model" ;
FLUT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FLUTC(time, lat, lon) ;
FLUTC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FLUTC:units = "W/m2" ;
FLUTC:long_name = "Clearsky upwelling longwave flux at top of model" ;
FLUTC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FREQI(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
FREQI:mdims = 1 ;
FREQI:units = "fraction" ;
FREQI:long_name = "Fractional occurrence of ice" ;
FREQI:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FREQL(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
FREQL:mdims = 1 ;
FREQL:units = "fraction" ;
FREQL:long_name = "Fractional occurrence of liquid" ;
FREQL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FREQR(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
FREQR:mdims = 1 ;
FREQR:units = "fraction" ;
FREQR:long_name = "Fractional occurrence of rain" ;
FREQR:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FREQS(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
FREQS:mdims = 1 ;
FREQS:units = "fraction" ;
FREQS:long_name = "Fractional occurrence of snow" ;
FREQS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSDS(time, lat, lon) ;
FSDS:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSDS:units = "W/m2" ;
FSDS:long_name = "Downwelling solar flux at surface" ;
FSDS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSDSC(time, lat, lon) ;
FSDSC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSDSC:units = "W/m2" ;
FSDSC:long_name = "Clearsky downwelling solar flux at surface" ;
FSDSC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNS(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNS:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNS:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNS:long_name = "Net solar flux at surface" ;
FSNS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNSC(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNSC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNSC:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNSC:long_name = "Clearsky net solar flux at surface" ;
FSNSC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNT(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNT:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNT:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNT:long_name = "Net solar flux at top of model" ;
FSNT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNTC(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNTC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNTC:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNTC:long_name = "Clearsky net solar flux at top of model" ;
FSNTC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNTOA(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNTOA:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNTOA:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNTOA:long_name = "Net solar flux at top of atmosphere" ;
FSNTOA:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSNTOAC(time, lat, lon) ;
FSNTOAC:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSNTOAC:units = "W/m2" ;
FSNTOAC:long_name = "Clearsky net solar flux at top of atmosphere" ;
FSNTOAC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float FSUTOA(time, lat, lon) ;
FSUTOA:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
FSUTOA:units = "W/m2" ;
FSUTOA:long_name = "Upwelling solar flux at top of atmosphere" ;
FSUTOA:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float H2O2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
H2O2_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
H2O2_SRF:long_name = "H2O2 in bottom layer" ;
H2O2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float H2SO4_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
H2SO4_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
H2SO4_SRF:long_name = "H2SO4 in bottom layer" ;
H2SO4_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ICEFRAC(time, lat, lon) ;
ICEFRAC:units = "fraction" ;
ICEFRAC:long_name = "Fraction of sfc area covered by sea-ice" ;
ICEFRAC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ICIMR(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
ICIMR:mdims = 1 ;
ICIMR:units = "kg/kg" ;
ICIMR:long_name = "Prognostic in-cloud ice mixing ratio" ;
ICIMR:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ICWMR(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
ICWMR:mdims = 1 ;
ICWMR:units = "kg/kg" ;
ICWMR:long_name = "Prognostic in-cloud water mixing ratio" ;
ICWMR:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float IWC(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
IWC:mdims = 1 ;
IWC:units = "kg/m3" ;
IWC:long_name = "Grid box average ice water content" ;
IWC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float LANDFRAC(time, lat, lon) ;
LANDFRAC:units = "fraction" ;
LANDFRAC:long_name = "Fraction of sfc area covered by land" ;
LANDFRAC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float LHFLX(time, lat, lon) ;
LHFLX:units = "W/m2" ;
LHFLX:long_name = "Surface latent heat flux" ;
LHFLX:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float LWCF(time, lat, lon) ;
LWCF:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
LWCF:units = "W/m2" ;
LWCF:long_name = "Longwave cloud forcing" ;
LWCF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float NUMICE(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
NUMICE:mdims = 1 ;
NUMICE:units = "1/kg" ;
NUMICE:long_name = "Grid box averaged cloud ice number" ;
NUMICE:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float NUMLIQ(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
NUMLIQ:mdims = 1 ;
NUMLIQ:units = "1/kg" ;
NUMLIQ:long_name = "Grid box averaged cloud liquid number" ;
NUMLIQ:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float OCNFRAC(time, lat, lon) ;
OCNFRAC:units = "fraction" ;
OCNFRAC:long_name = "Fraction of sfc area covered by ocean" ;
OCNFRAC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float OMEGA(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
OMEGA:mdims = 1 ;
OMEGA:units = "Pa/s" ;
OMEGA:long_name = "Vertical velocity (pressure)" ;
OMEGA:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float OMEGAT(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
OMEGAT:mdims = 1 ;
OMEGAT:units = "K Pa/s" ;
OMEGAT:long_name = "Vertical heat flux" ;
OMEGAT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ORO(time, lat, lon) ;
ORO:units = "frac" ;
ORO:long_name = "ORO" ;
ORO:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PBLH(time, lat, lon) ;
PBLH:units = "m" ;
PBLH:long_name = "PBL height" ;
PBLH:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PHIS(time, lat, lon) ;
PHIS:units = "m2/s2" ;
PHIS:long_name = "Surface geopotential" ;
float PRECC(time, lat, lon) ;
PRECC:units = "m/s" ;
PRECC:long_name = "Convective precipitation rate (liq + ice)" ;
PRECC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PRECL(time, lat, lon) ;
PRECL:units = "m/s" ;
PRECL:long_name = "Large-scale (stable) precipitation rate (liq + ice)" ;
PRECL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PRECSC(time, lat, lon) ;
PRECSC:units = "m/s" ;
PRECSC:long_name = "Convective snow rate (water equivalent)" ;
PRECSC:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PRECSL(time, lat, lon) ;
PRECSL:units = "m/s" ;
PRECSL:long_name = "Large-scale (stable) snow rate (water equivalent)" ;
PRECSL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PS(time, lat, lon) ;
PS:units = "Pa" ;
PS:long_name = "Surface pressure" ;
PS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float PSL(time, lat, lon) ;
PSL:units = "Pa" ;
PSL:long_name = "Sea level pressure" ;
PSL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float Q(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
Q:mdims = 1 ;
Q:units = "kg/kg" ;
Q:long_name = "Specific humidity" ;
Q:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float QFLX(time, lat, lon) ;
QFLX:units = "kg/m2/s" ;
QFLX:long_name = "Surface water flux" ;
QFLX:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float QREFHT(time, lat, lon) ;
QREFHT:units = "kg/kg" ;
QREFHT:long_name = "Reference height humidity" ;
QREFHT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float QRL(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
QRL:mdims = 1 ;
QRL:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
QRL:units = "K/s" ;
QRL:long_name = "Longwave heating rate" ;
QRL:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float QRS(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
QRS:mdims = 1 ;
QRS:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
QRS:units = "K/s" ;
QRS:long_name = "Solar heating rate" ;
QRS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float RELHUM(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
RELHUM:mdims = 1 ;
RELHUM:units = "percent" ;
RELHUM:long_name = "Relative humidity" ;
RELHUM:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SHFLX(time, lat, lon) ;
SHFLX:units = "W/m2" ;
SHFLX:long_name = "Surface sensible heat flux" ;
SHFLX:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SNOWHICE(time, lat, lon) ;
SNOWHICE:units = "m" ;
SNOWHICE:long_name = "Snow depth over ice" ;
SNOWHICE:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SNOWHLND(time, lat, lon) ;
SNOWHLND:units = "m" ;
SNOWHLND:long_name = "Water equivalent snow depth" ;
SNOWHLND:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SO2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
SO2_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
SO2_SRF:long_name = "SO2 in bottom layer" ;
SO2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SOAG_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
SOAG_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
SOAG_SRF:long_name = "SOAG in bottom layer" ;
SOAG_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SOLIN(time, lat, lon) ;
SOLIN:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
SOLIN:units = "W/m2" ;
SOLIN:long_name = "Solar insolation" ;
SOLIN:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float SWCF(time, lat, lon) ;
SWCF:Sampling_Sequence = "rad_lwsw" ;
SWCF:units = "W/m2" ;
SWCF:long_name = "Shortwave cloud forcing" ;
SWCF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float T(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
T:mdims = 1 ;
T:units = "K" ;
T:long_name = "Temperature" ;
T:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TAUX(time, lat, lon) ;
TAUX:units = "N/m2" ;
TAUX:long_name = "Zonal surface stress" ;
TAUX:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TAUY(time, lat, lon) ;
TAUY:units = "N/m2" ;
TAUY:long_name = "Meridional surface stress" ;
TAUY:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TGCLDCWP(time, lat, lon) ;
TGCLDCWP:units = "kg/m2" ;
TGCLDCWP:long_name = "Total grid-box cloud water path (liquid and ice)" ;
TGCLDCWP:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TGCLDIWP(time, lat, lon) ;
TGCLDIWP:units = "kg/m2" ;
TGCLDIWP:long_name = "Total grid-box cloud ice water path" ;
TGCLDIWP:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TGCLDLWP(time, lat, lon) ;
TGCLDLWP:units = "kg/m2" ;
TGCLDLWP:long_name = "Total grid-box cloud liquid water path" ;
TGCLDLWP:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TMQ(time, lat, lon) ;
TMQ:units = "kg/m2" ;
TMQ:long_name = "Total (vertically integrated) precipitable water" ;
TMQ:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TREFHT(time, lat, lon) ;
TREFHT:units = "K" ;
TREFHT:long_name = "Reference height temperature" ;
TREFHT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TS(time, lat, lon) ;
TS:units = "K" ;
TS:long_name = "Surface temperature (radiative)" ;
TS:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float TSMN(time, lat, lon) ;
TSMN:units = "K" ;
TSMN:long_name = "Minimum surface temperature over output period" ;
TSMN:cell_methods = "time: minimum" ;
float TSMX(time, lat, lon) ;
TSMX:units = "K" ;
TSMX:long_name = "Maximum surface temperature over output period" ;
TSMX:cell_methods = "time: maximum" ;
float U(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
U:mdims = 1 ;
U:units = "m/s" ;
U:long_name = "Zonal wind" ;
U:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float U10(time, lat, lon) ;
U10:units = "m/s" ;
U10:long_name = "10m wind speed" ;
U10:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float UU(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
UU:mdims = 1 ;
UU:units = "m2/s2" ;
UU:long_name = "Zonal velocity squared" ;
UU:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float V(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
V:mdims = 1 ;
V:units = "m/s" ;
V:long_name = "Meridional wind" ;
V:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float VD01(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
VD01:mdims = 1 ;
VD01:units = "kg/kg/s" ;
VD01:long_name = "Vertical diffusion of Q" ;
VD01:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float VQ(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
VQ:mdims = 1 ;
VQ:units = "m/skg/kg" ;
VQ:long_name = "Meridional water transport" ;
VQ:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float VT(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
VT:mdims = 1 ;
VT:units = "K m/s" ;
VT:long_name = "Meridional heat transport" ;
VT:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float VU(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
VU:mdims = 1 ;
VU:units = "m2/s2" ;
VU:long_name = "Meridional flux of zonal momentum" ;
VU:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float VV(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
VV:mdims = 1 ;
VV:units = "m2/s2" ;
VV:long_name = "Meridional velocity squared" ;
VV:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float WGUSTD(time, lat, lon) ;
WGUSTD:units = "m/s" ;
WGUSTD:long_name = "wind gusts from turbulence" ;
WGUSTD:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float WSUB(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
WSUB:mdims = 1 ;
WSUB:units = "m/s" ;
WSUB:long_name = "Diagnostic sub-grid vertical velocity" ;
WSUB:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float Z3(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
Z3:mdims = 1 ;
Z3:units = "m" ;
Z3:long_name = "Geopotential Height (above sea level)" ;
Z3:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float bc_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
bc_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
bc_a1_SRF:long_name = "bc_a1 in bottom layer" ;
bc_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float dst_a1SF(time, lat, lon) ;
dst_a1SF:units = "kg/m2/s" ;
dst_a1SF:long_name = "dst_a1 dust surface emission" ;
dst_a1SF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float dst_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
dst_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
dst_a1_SRF:long_name = "dst_a1 in bottom layer" ;
dst_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float dst_a3SF(time, lat, lon) ;
dst_a3SF:units = "kg/m2/s" ;
dst_a3SF:long_name = "dst_a3 dust surface emission" ;
dst_a3SF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float dst_a3_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
dst_a3_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
dst_a3_SRF:long_name = "dst_a3 in bottom layer" ;
dst_a3_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ncl_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
ncl_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
ncl_a1_SRF:long_name = "ncl_a1 in bottom layer" ;
ncl_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ncl_a2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
ncl_a2_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
ncl_a2_SRF:long_name = "ncl_a2 in bottom layer" ;
ncl_a2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float ncl_a3_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
ncl_a3_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
ncl_a3_SRF:long_name = "ncl_a3 in bottom layer" ;
ncl_a3_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float num_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
num_a1_SRF:units = " 1/kg" ;
num_a1_SRF:long_name = "num_a1 in bottom layer" ;
num_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float num_a2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
num_a2_SRF:units = " 1/kg" ;
num_a2_SRF:long_name = "num_a2 in bottom layer" ;
num_a2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float num_a3_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
num_a3_SRF:units = " 1/kg" ;
num_a3_SRF:long_name = "num_a3 in bottom layer" ;
num_a3_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float pom_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
pom_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
pom_a1_SRF:long_name = "pom_a1 in bottom layer" ;
pom_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float so4_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
so4_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
so4_a1_SRF:long_name = "so4_a1 in bottom layer" ;
so4_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float so4_a2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
so4_a2_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
so4_a2_SRF:long_name = "so4_a2 in bottom layer" ;
so4_a2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float so4_a3_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
so4_a3_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
so4_a3_SRF:long_name = "so4_a3 in bottom layer" ;
so4_a3_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float soa_a1_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
soa_a1_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
soa_a1_SRF:long_name = "soa_a1 in bottom layer" ;
soa_a1_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
float soa_a2_SRF(time, lat, lon) ;
soa_a2_SRF:units = "kg/kg" ;
soa_a2_SRF:long_name = "soa_a2 in bottom layer" ;
soa_a2_SRF:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
// global attributes:
:Conventions = "CF-1.0" ;
:source = "CAM" ;
:case = "f2000.T31T31.control" ;
:title = "UNSET" ;
:logname = "hanbre" ;
:host = "hexagon-5" ;
:Version = "$Name$" ;
:revision_Id = "$Id$" ;
:initial_file = "/work/hanbre/inputdata/atm/cam/inic/gaus/cami_0000-01-01_48x96_L30_c100426.nc" ;
:topography_file = "/work/hanbre/inputdata/atm/cam/topo/USGS-gtopo30_48x96_c050520.nc" ;
}
It contains information about variables (names, dimensions, units) and also global attributes (conventions, source, etc.).
Dimensions
- N-dimensional arrays have sizes, or “shape”
- Dimensions are names for array sizes in the file
- Are integer values
- One dimension may be “unlimited”: * arrays allowed to grow along that dimension *all other dimensions are fixed
dimensions:
lat = 48 ;
lon = 96 ;
time = UNLIMITED ; // (30 currently)
nbnd = 2 ;
chars = 8 ;
lev = 30 ;
ilev = 31 ;
Variables
float T(time, lev, lat, lon) ;
T:mdims = 1 ;
T:units = "K" ;
T:long_name = "Temperature" ;
T:cell_methods = "time: mean" ;
- Variables are arrays of data
- Have type (float, etc.), shape (time,lat,lon), attributes/metadata (units, long_name, etc.)
Coordinate variable definition
double time(time) ;
time:long_name = "time" ;
time:units = "days since 0001-01-01 00:00:00" ;
time:calendar = "noleap" ;
time:bounds = "time_bnds" ;
int date(time) ;
date:long_name = "current date (YYYYMMDD)" ;
int datesec(time) ;
datesec:long_name = "current seconds of current date" ;
double lat(lat) ;
lat:long_name = "latitude" ;
lat:units = "degrees_north" ;
double lon(lon) ;
lon:long_name = "longitude" ;
lon:units = "degrees_east" ;
- one dimensional variable
- dimension name is the same as the variable name
- must be numeric (integer, float, double)
- must be monotonic (increasing or decreasing)
- examples: variable_name(dimension_name)
- lon(lon), lat(lat), plevel(plevel), time(time)
- the first lon is the variable name and the second is the variable dimention!
- Usage: variable T(time, lev, lat, lon)
- T(0,0,i,j) is temperature at ith, jth element for time=0 and lev=0
- latitude of that element is value at lat(i)
- longitude of the element is value at lon(j)
- T(:,3:10,10:12,24:27) allows to get a sub-array: all the time, level from 3 to 10, latitudes from index 10 to 12 and longitude from 24 to 27
NetCDF conventions
netCDF is a very flexible data format; so flexible that we usually follow some conventions:
- makes data comparison easier
- facilitates development of viewing (eg: ncview) and processing tools (NetCDF Operators; Climate Data Op.)
COARDS (1995; frozen) convention
- Cooperative Ocean/Atmosphere Research Data Service
- created for rectilinear grids
- http://ferret.wrc.noaa.gov/noaa_coop/coop_cdf_profile.html
CF (2005/2006; continues to evolve) convention
- Climate and Forecast Metadata Convention (1.0 -> 1.6)
- generalizes and extends the COARDS convention
- much more complex; curvilinear and unstructured grids
- calendar attributes (eg: no_leap, 360_day, 365_day,..)
- http://cf-pcmdi.llnl.gov/
Most climate related data archives use NetCDF and adhere to these conventions: eg: CMIP5, CMIP3, CESM, IPCC. etc.
CESM CAM 5.3 follows CF conventions.
NCL variables
All NCL variables look like NetCDF variables. They have names, types, shape, size and values. They may also have additional information (metadata) such as a long name, units, names of dimensions, etc.
Let’s define a vector with 3 values:
aInt = (/1,2,3/)
print(aInt)
(/ is used to specify the start of your vector and /) deontes the end of your array. Here we created a vector containing 3 values: 1, 2 and 3. If we print aInt, we will get information on aInt NCL variable:
Variable: aInt
Type: integer
Total Size: 12 bytes
3 values
Number of Dimensions: 1
Dimensions and sizes: [3]
Coordinates:
(0) 1
(1) 2
(2) 3
To create a two-dimensional array:
m2D = (/(/1.00,1.00,1.00/),(/0.9,0.80,0.50/)/)
print(m2D)
Variable: m2D
Type: float
Total Size: 24 bytes
6 values
Number of Dimensions: 2
Dimensions and sizes: [2] x [3]
Coordinates:
(0,0) 1
(0,1) 1
(0,2) 1
(1,0) 0.9
(1,1) 0.8
(1,2) 0.5
In these two examples, we do not have additional metadata (properties of our variables). Metadata (attributes) can be added using the syntax @:
m2D@units = "degC"
m2D@long_name = "matrix example"
print(m2D)
Variable: m2D
Type: float
Total Size: 24 bytes
6 values
Number of Dimensions: 2
Dimensions and sizes: [2] x [3]
Coordinates:
Number Of Attributes: 2
long_name : matrix example
units : degC
(0,0) 1
(0,1) 1
(0,2) 1
(1,0) 0.9
(1,1) 0.8
(1,2) 0.5
You can see that we now have two attributes when we print m2D.
Detailed Look at an NCL Variable
Let’s take one history file generated by the CAM model. We use addfile to open the netCDF file:
; open netCDF file to read
f=addfile("f2000.T31T31.control.cam.h0.0008-12-22-00000.nc","r")
; import variable ( STRUCTURE )
T = f->T
-
The second argument of
addfileallows to specify if you want to read (“r”) or write (“w”). -
If you do not know the names of variables, you can print the file handler (f):
print(f)
For the comparison of different simulations or the joint analysis of ensemble simulations, it is very useful to access multiple files at once. The function addfiles can open multiple existing data files or create multiple new data files using one of the supported file formats.
list_of_files = systemfunc("ls *.nc") ; NetCDF file names
f = addfiles(list_of_files, "r") ; data type `list`
- Use printVarSummary to get summary information on yoru variable:
; variable overview
printVarSummary (T)
Variable: T
Type: float
Total Size: 6082560 bytes
1520640 values
Number of Dimensions: 4
Dimensions and sizes: [time | 11] x [lev | 30] x [lat | 48] x [lon | 96]
Coordinates:
time: [2910..2920]
lev: [3.64346569404006..992.556095123291]
lat: [-87.15909455586285..87.15909455586285]
lon: [ 0..356.25]
Number Of Attributes: 4
mdims : 1
units : K
long_name : Temperature
cell_methods : time: mean
- Use printMinMax to print the minimum and maximum values of a variable
; variable Min & Max values printMinMax (T, False)
(0) Temperature: min=176.799 max=311.035
The second argument is either True (line feed prior to printing the min/max values) or False (no line feed):
printMinMax (T, True)
(0)
(0) Temperature: min=176.799 max=311.035
Good to know
- semi-column (;) is used to comment your code. Everything after
;will be ignored.- addfile can read netCDF, grib, hdf and hdfeos data file format.
Detailed look at an NCL variable
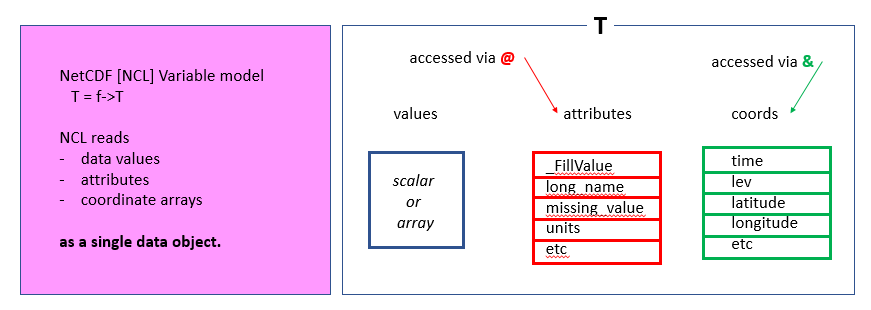
For instance, to get the list of times for T:
print(T&time)
Variable: time (coordinate)
Type: double
Total Size: 88 bytes
11 values
Number of Dimensions: 1
Dimensions and sizes: [time | 11]
Coordinates:
Number Of Attributes: 4
long_name : time
units : days since 0001-01-01 00:00:00
calendar : noleap
bounds : time_bnds
(0) 2910
(1) 2911
(2) 2912
(3) 2913
(4) 2914
(5) 2915
(6) 2916
(7) 2917
(8) 2918
(9) 2919
(10) 2920
And to get the units:
print(T@units)
(0) K
Key Points
NCL and its netCDF data model